Lebanon: How safe is our water

Although Lebanon is considered to have an excess in water resources unlike the other Arab countries, the water sector in Lebanon is suffering from a variety of management and technical restriction. In Lebanon, like other countries, the water quality is affected by many anthropogenic sources including domestic, industrial and agricultural wastewater discharges.
In agricultural uses, the excessive use of fertilizers has to lead the nitrate to penetrate into the groundwater and rivers and affects its quality. The untreated industrial effluents impinged the quality of water due to the chemicals, heavy metals and organic liquid effluents that leak into the rivers, the Mediterranean Sea, and groundwater. Also, the Lebanese domestic wastewater is being discharged into the rivers then the sea without any treatment. Finally, the overwhelming waste crisis accompanied with open air dumping caused an exponentially increasing infection in the Lebanese waste water. All of these factors led to the contamination of the drinking water and rivers.
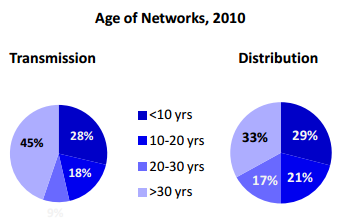
Some studies on the quality of water showed that the water has a high concentration of BOD5, the presence of Escherichia coli, and total coliforms (Geara-Matta et Al. 2010). Furthermore, the old infrastructure (more than 30 years) of the governmental water treatment facility with its aged infrastructure is not reliable due to its ruined network which causes increasing leakage of water. The leakage percentage from the water supply network vary between 35 to 50% according to the age of the network (shown in figure 1). Also, this may lead to the leakage of the wastewater into the drinking water network (Council of Development and Reconstruction 2015).
Figure 1: Age of the transmission and distribution networks done in 2010 (Bassil 2010)
As a result of all these problems, the water resources present in Lebanon must overcome an appropriate treatment depending on the nature of water and the contaminants that contain. This treatment will enhance the public health that is basically related to the quality of water regarding drinking water, hygiene and sanitation.
A large number of constraints faced in Lebanon justifies the lack of water treatment plants in the country. The high capital cost (cost of the equipment), as well as the high operating cost (mainly the cost of the power needed to aliment the high-pressure pumps), are imposed by the water treatment companies. These consulting and contracting companies execute a monopoly in Lebanon. Furthermore, there is a lack of studies that try to optimize the water treatment plants and to satisfy the needs of the Lebanese population.
Therefore, this begs the need to develop a model to optimize the design aspects of water while reducing the capital and operating cost, thereby motivating a large fraction of people to invest in water treatment system rather than drinking water from untrustworthy sources at the expense of large financial investment.
This will eventually reduce waterborne diseases leading to a healthier society.